What Is a Data Center?
A data center is a space to accommodate machinery, especially computer equipment and storage devices It also accommodates dedicated servers for your business. These centers are essential for various organizations. They are small businesses, large corporations, and cloud service providers. The data centers are classified as Tier 1, Tier 2, Tier 3, and Tier 4. Tier 1 data center is the simplest form and Tier 4 is the most updated.
What Is the History of a Data Center?
The first data centers were seen in the early 1940s when the centers were used as huge computer rooms. The building costs of a data center are high and so is its maintenance. The use of data centers sky-rocketed during the dot-com bubble between 1997-2000. To enhance performance and energy efficiency, modernization of the data center is important. Also, with the rise of the internet, many companies began operating data centers. The increased demand for online services led to the necessity of data storage. After 2000, some companies introduced cloud computing. They allow businesses to rent storage space instead of maintaining their physical servers. It enabled the creation of virtual data servers. This reduced reliance on maintaining physical hardware.
The security of the data centers is of utmost importance. Physical access is only permitted if you have the correct Email ID and password. Fencing and mantraps are some of the primary security measures taken. Other than that, you can expect continuous video surveillance, CCTV monitoring, and an active alarm system. After 2010, there is an increase in hyper-scale data centers. They handle huge quantities of data and resources for global clients. Also, many business owners begin to prioritize their company's data security. So, the use of dedicated servers begin to rise in the data center for data privacy.
What Are the Different Tiers of Data Centers?
The following tiers of data centers are essential for housing your North American dedicated servers:
- Tier 1: A tier 1 data center provides basic infrastructure for supporting an IT system. It has 99.671% Uptime and has 1729 minutes of downtime per annum. It is suitable for small businesses with low IT needs.
- Tier 2: You will get redundant infrastructure, uptime of 99.741%, and 1361 minutes (22.68 hours) of downtime.
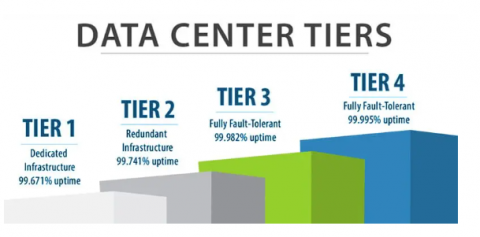
- Tier 3: All the facilities from Tier 1 and Tier 2 are available in Tier 3. It has dual power and data center cooling distribution paths. It has redundant systems that allow any component maintenance without affecting operations. Additionally, there are more data paths and backup equipment which will reduce the downtime significantly. 99.982% is the minimum uptime you will get with a Tier 3 data center. The downtime is only 95 minutes per year. This is significantly less than the 1361 minutes per annum in Tier 2.
- Tier 4: This is the highest level of the data center. This type of data center has fault-tolerance capabilities with 99.995% uptime and a maximum of 26 minutes of downtime per annum.
All the small-scaled business clients go for Tier 1 data centers. These are way less expensive than Tier 2, Tier 3, and Tier 4 data centers. That makes sense for the server providers who have small-scale businesses as their clients. Such clients will look for cheaper servers to host their websites online. This can be a cost-effective solution for small businesses. The Tier 1 data centers are mainly used for colocation.
The data centers bring with them a dynamic infrastructure. They help secure and automatic workload movements across a data center. There are certain side benefits associated with data center infrastructure. It also enables cloud and grid computing.
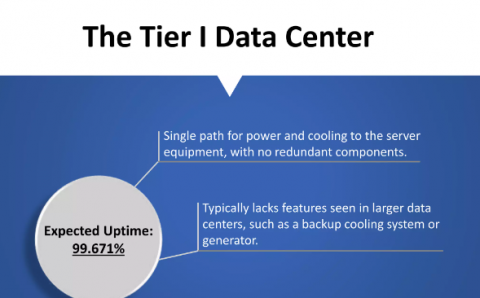
What Are the Characteristics of a Tier 1 Data Center?
The most basic form of a data center is the Tier 1 form. You can classify it as the basic-intermediate level of a data center. To be called a Tier 1 data center, the center has to adhere to the following:
- Single Points of Failure: Tier 1 servers are prone to single failure points. So, it is important to maintain each component. This includes its power, cooling and network.
- 99.671% Uptime Per Year: You can expect a minimum of 99.671% uptime per annum. This helps in maintaining dedicated server stability of small and medium businesses. So, your company carries out daily functions without any online disruption.
- Zero redundancy: The tier 1 data centers don’t have any kind of redundancies on any part of the system’s operations.
- Single Power And Cooling Distribution Path: There is only one cooling and power distribution path. So, the failure of power or cooling systems leads to data center downtime. Also, there are uninterruptible power supply systems to protect against power losses.
- Low Cost: They are less expensive to build and require low maintenance. They are suitable for smaller businesses that have low budgets.
- Basic Security Measures: They have basic security measures including physical security. These include system locks and surveillance measures.
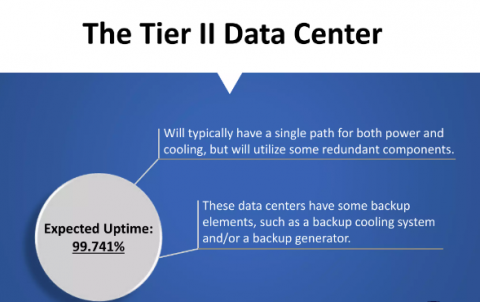
What Are the Characteristics of a Tier 2 Data Center?
Some features of Tier 2 Data Centers are
- Reductant Capacity Components: Tier 2 data centers have redundancy for various critical systems. These include power and cooling and are configured as N + 1. N is the capacity required to support a data center’s operations. + 1 is referred to as an additional backup component.
- Improved Uptime: These data centers provide an expected uptime of 99.741%. Your Asian dedicated server's higher uptime builds customer trust.
- Single Power And Cooling Path: They depend on a single distribution path for cooling and power. Although some components have backups, a fault in the key distribution path causes downtime.
- Protection from Failures: They provide greater protection than Tier 1 against hardware faults and power cuts. Data center servers can handle critical failures from previous-tier servers.
- Moderate Cost: They are cost-effective for small and medium-scale businesses. These data centers provide full redundancy and fault tolerance.
- Security: They have stronger security measures than Tier 1 servers. Your company’s data will be safe in the Tier 2 data center.
- Use Case: It benefits small businesses that can tolerate some downtime. However, they need better protection against systematic failures.
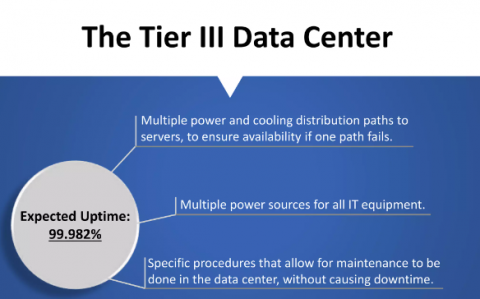
What Are the Characteristics of a Tier 3 Data Center?
Some features of a Tier 3 Data Center are:
- Maintainable: These data centers are designed to allow maintenance of any component. This is done without disrupting a system’s operation.
- Redundant Cooling Paths And Power: This data center has a minimum of two cooling center paths. One path is active at any time. Another path serves as a backup if the primary path fails.
- Higher Availability And Uptime: These data centers have an expected uptime of 99.982%. This higher uptime ensures crucial operations with low disruptions.
- Fault Tolerance: This data center’s design ensures planned maintenance and upgradation without impacting an operation’s facility.
- Backup Power Systems: They have backup generators that provide machinal power during power outages.
- Improved Security: They have advanced security measures. This includes biometric access and surveillance. It prevents unauthorized access to your company’s system. As a result, it maintains Europe dedicated server security.
What Are the Characteristics of a Tier 4 Data Center?
Some features of Tier 4 data centers are:
- Total Fault Tolerant: They are fully fault tolerant. This means they can continue to operate even if critical infrastructure fails. They have a backup for cooling, power or network systems.
- Multiple Cooling Paths: A Tier 4 data center has both cooling distribution paths and dual powers. Both paths can handle the data center’s entire load. Also, if one path fluctuates, another path gets activated.
- Highest Uptime: It offers an expected uptime of 99.995%. It has the highest upkeep levels across all data centers. This helps your Oceania dedicated server's stability and smooth execution of workplace tasks.
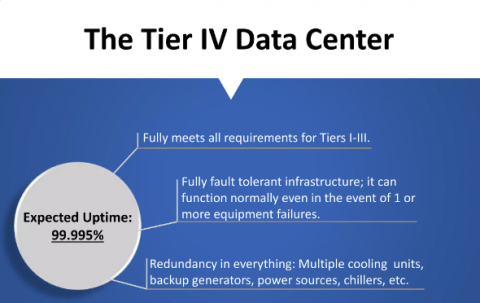
- Concurrent Maintainability: You can perform system maintenance without any downtime. If there is a failure in one system, another system starts automatically.
- Advanced Cooling Systems: It has advanced cooling systems. This ensures that the equipment remains within a safe temperature and humidity range.
- No Single Failure Points: Every crucial component has an independent backup. This applies to cooling, networking and power.
- High Cost And Complex: They are very expensive to build due to advanced equipment requirements. Also, continuous maintenance costs need high capital. Also, its complex infrastructure requires highly skilled personnel for maintenance.
Summary
The definition of a data center and its various types are written here. First, there is an explanation of the history of data centers. The usage of data centers increased during the 90s. The reason is that companies prioritize a safe storage space for business data. Also, there was an introduction of cloud computing services. This enabled businesses to rent storage spaces from a cloud service provider. After that, the various types of data servers are written in brief. Tier 1 data center is suitable for small and medium-sized businesses. Tier 2 data center has better facilities than Tier 1 servers. They have stronger power fault tolerance capabilities than the previous tier. Apart from this, Tier 3 data center has higher uptime and backup systems. This is suitable for large companies that need to preserve huge information. At last, the Tier 4 data center was explained. It has the highest uptime, advanced cooling systems and is fully fault tolerant. This server is suitable for conducting international business. Installation of an Africa-dedicated server or other location in your data center is essential. It keeps your business data secured from hackers.
CTA
Get the best-dedicated servers for your business from our Tier IV data centers.
Closing Thoughts
A data center is becoming an important part of today’s businesses. They are built to protect systems from data thefts. You can set passwords, biometric security or cameras to protect your critical information. There are four tiers of data centers. You can choose your preferred center as per your business needs. Also, install a dedicated server in your data center for data privacy.
Blog Category:
- Abhik's blog
- Log in or register to post comments



