RAID levels carry the identity of the RAID system.
RAID is essential to improve your dedicated server storage system. You need a dedicated server to build your company website.
Your website needs to have different resources. The most important of those resources are various multimedia files. These files contain images and videos, in general.
It also can have other important resources in different file types. Those important files are CSS, HTML, and JavaScript. Server storage helps your website have all those resources.
Now, dedicated server storage is also essential for keeping your data safe and secure.
A website is nothing without its data. Your website gets a distinct identity through its data. The dedicated server storage helps you save, manage, and recover important website data. So, your website’s dedicated server needs an ideal storage capacity.
Your website’s data, system files, and applications stay safe and secure in the storage space. Still, you might face the risk of potential data loss due to many technical reasons. RAID helps you to stay worry-free from such issues in dedicated server storage.

Different RAID types strengthen the utility of the RAID system. RAID hard drives in a dedicated server function through these levels. They increase performance with the redundancy aspect of this technology.
You will learn everything about RAID array levels in this blog post.
This will help you to choose the best RAID level for your dedicated server storage.
In this blog, you will learn about:
Detailed Overview of RAID 2, 3, 4
Detailed Overview of RAID 50, 60
RAID Levels and Their Advantages
RAID Levels and Their Disadvantages
So, let’s jump straight to it!
What Is RAID?
Before knowing about RAID levels, you should know a little more about its system.
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. This technological system takes many physical hard drives in a single logical unit. This improves reliability in the data storage. This also optimizes performance and capacity in computer systems.
This also benefits the dedicated server systems more. You can set RAID arrays to circulate data across many disks. This helps enhance different aspects of the dedicated server storage.

It copies your data from one hard drive to store it in another. So, it also gives you data protection facilities.
But that doesn’t make it some kind of backup technology.
It upgrades the server storage with incredible functions. And RAID array levels help your dedicated server storage perform better.
What Are RAID Levels?
RAID levels are different but important structures in a RAID system. They build the behavior and qualities of a RAID storage system in dedicated hosting. These levels arrange and manage many physical disks in the system.
Each of these levels comes with a unique method of combining the disks. This helps the disks meet various purposes of storage space. This improves data redundancy and storage performance. It also increases the storage capacity, strengthening the utilities of RAID.
RAID array levels in storage work through some important functions. They distribute data across the disks for better management. They also check on the system in a dedicated server to manage disk failures. They also make redundancy happen in the system.
The levels also decide how the RAID system will perform in various operations. They check out on read and write operations. They look for the array working on the total usable storage space. They also ensure a strong dedicated server storage system against hardware failures.
RAID levels in storage are vital to understand how RAID arrays work. Each level comes with balancing among different RAID system functions. Those are performance, storage efficiency, and data protection. These levels provide a structure to select a suitable setup.
These setups depend on the particular needs and priorities of a system. Those needs and priorities range from data protection to fast access times. They also focus on the most effective use of accessible storage resources.
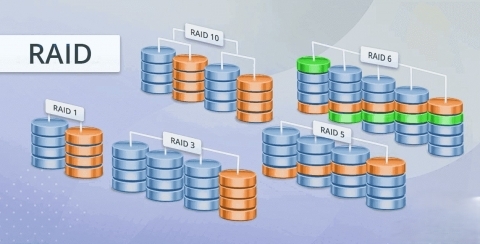
Types of RAID Levels
There are three types of RAID levels: 1) Common, 2) Rare, and 3) Advanced.
RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, and 10 (1+0) fall under the first type of RAID.
Rare RAID levels are RAID 2, 3, and 4.
Advanced RAID levels are RAID 30 (3+0), 50 (5+0), and 60 (6+0).
A Detailed Overview of RAID 0
Functions: In RAID levels, RAID 0 works through striping. This level works by dividing data into blocks. It writes the data across many disks in parallel. It then shares these blocks across many disks in a serial manner.
A typical stripe size, which is the size of each block, ranges from 16 KB to 128 KB. It can also take up more size depending on the workload.
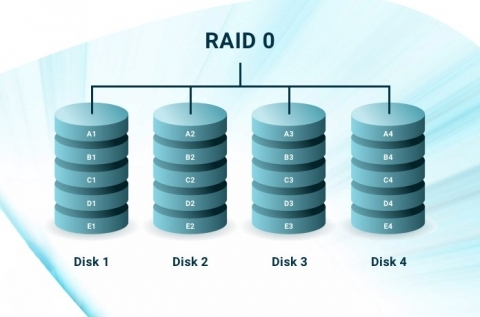
Data distribution across many disks makes accessing data easier. The system can get different parts of data at once from several disks. This also increases the total data throughput in a dedicated server system. This is because data read or write from a lot of disks happens at the same time.
Use Case: It is perfect for applications running on dedicated servers that need high speed. Video editing applications are one such example. But it doesn’t provide any critical data protection facilities.
A Detailed Overview of RAID 1
Functions: RAID 1 is an essential RAID level known for the mirroring function. In this setup, the same data gets copied to two or more disks at the same time. Mirroring is also another name for this act of copying. It takes every piece of data stored on the dedicated server written to the array. It then duplicates them to store on two or more disks. So, each disk in the RAID 1 array has the same copy of the data.
It also provides the best read and write speeds for data in the dedicated servers. The system can get the data from any disk with the read operations. Having identical data makes accessing data from any disk easier for the system. The system also writes the data to all disks in this RAID array at once. Each disk gets the same data at the same time. This ensures that all disks stay identical.
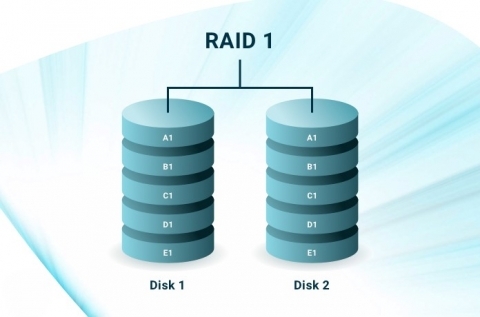
This RAID array level also offers peak fault tolerance due to mirroring. So, in case of disk failure, the system runs using the data in the other disks. This doesn’t cause any interruption to the process in dedicated servers.
Use Case: RAID 1 is perfect for applications where data redundancy is important. Financial data storage is an example of that. This RAID level in storage is also useful for database dedicated servers.
A Detailed Overview of RAID 5
Functions: RAID 5 divides the data into blocks, and then stripes that across all disks in the array. It integrates parity information along with the data blocks. So, the main function of this RAID level is striping with parity.
Parity is a type of data that checks for errors. It rebuilds the original data in case of disk failure in dedicated servers. It doesn’t store data on a single disk. It distributes data across all the disks in the array.
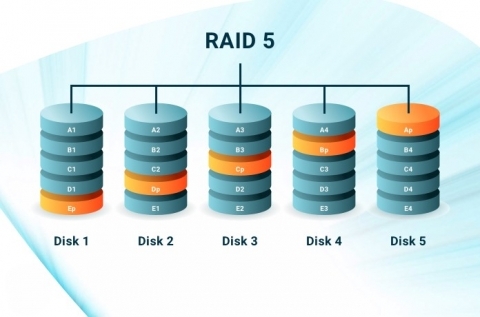
The system calculates the parity while writing the data in a RAID 5 array. It takes all the data in the other blocks. Then, it stores the data in a specific location on a different disk from the data itself. The write process includes writing both the data and parallel parity blocks to the disks. The system can also access the data from the contained disks in dedicated servers. Due to striping, its system can read data from several disks at the same time. It only reads the parity data when a disk fails. This improves read performance, in general.
Use Case: This array is useful for file servers. Other applications that need a mix of redundancy and performance also use this array.
A Detailed Overview of RAID 6
Functions: This RAID level works data striping with dual parity. In striping, it divides and stripes the data across several disks. But it takes two independent parity blocks (P and Q) per stripe. It calculates both parity blocks using different algorithms. This makes the dedicated server system recover data in case of multi-disk failure. It also distributes dual parity across all disks in the array.
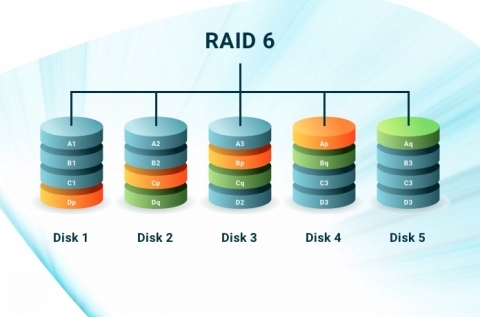
The data write process also follows the dual parity information. It calculates the P parity set like in RAID 5. But it takes a different mathematical formula to build the Q parity set. Both parity blocks get updated upon writing the new data. The read process follows the same method as RAID 5.
Use Case: This RAID is useful for dedicated servers where data protection is a priority. The systems dealing with the concern of various disk failures need the help of this array, too.
A Detailed Overview of RAID 10
Functions: RAID 1 and 0 make RAID 10 with their combining functions. So, it combines both striping and mirroring. It mirrors two RAID 0 arrays to run its operations.
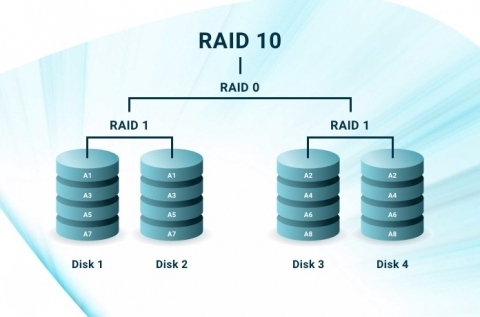
Use Case: It is ideal for high-performance databases that need both speed and redundancy.
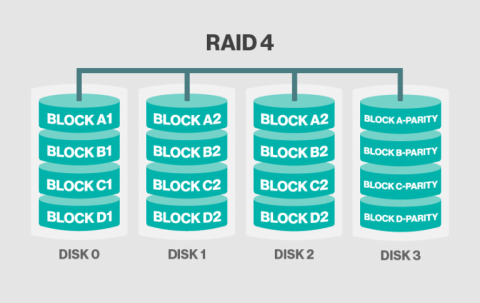
A Detailed Overview of RAID 2, 3, and 4
Functions: These RAID levels are less common to use.
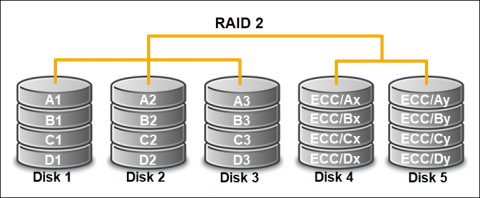
RAID 2 uses bit-level striping with Hamming code error correction. RAID 3 performs byte-level striping with dedicated parity. RAID 4 applies block-level striping with dedicated parity.
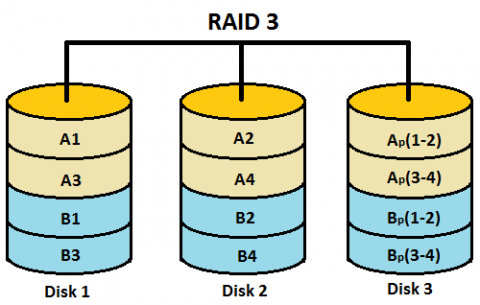
Use Case: The usage of these RAID array levels is very rare nowadays.
A Detailed Overview of RAID 30
Functions: This RAID level takes many RAID 3 arrays and stripes data across them. This provides striping for performance. It also delivers dedicated parity of RAID 3 for redundancy.
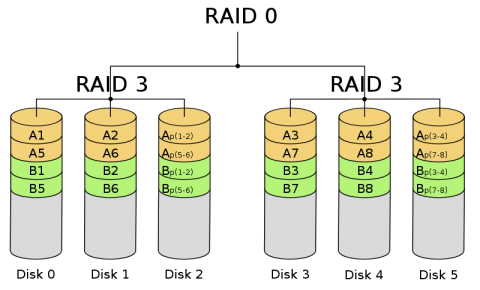
Use Case: It is important for applications that need high-speed sequential data processing with redundancy. Video editing or large-scale media production are some examples.
A Detailed Overview of RAID 50 and 60
The functions of both of these RAID levels are alike in RAID 30.
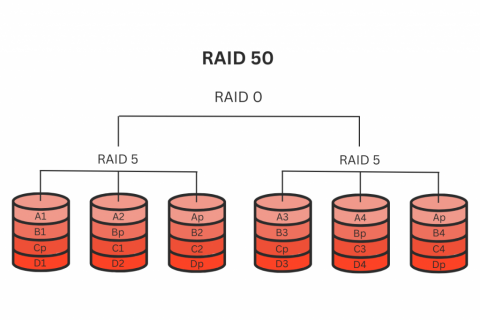
But they have different use cases.
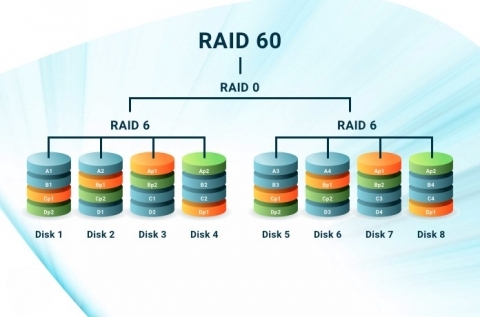
Use Case: RAID 50 is ideal for large-scale storage systems that run on high performance and fault tolerance. And RAID 60 is crucial for applications requiring peak redundancy and high availability. Both these different RAID types help make enterprise-level applications.
Advantages of Raid Levels
Here are the advantages of all the RAID levels:
| RAID Levels | Advantages |
| RAID 0 |
It provides high performance in dedicated servers with full storage capacity. The data read and write operation happens at the same time across several disks. It comes with a very easy and simple setup compared to other RAID array levels. |
| RAID 1 |
It gives you peak data redundancy through mirroring. It also simplifies the data recovery process if one disk fails in dedicated servers. The mirrored disks in this RAID hard drive increase system reliability in general. |
| RAID 5 |
Fault tolerance in the RAID 5 array distributes parity data. This helps restore lost data in case of a single disk failure in dedicated servers. It offers better storage performance than RAID 1. It only takes the space of one disk for parity. Also, its data redundancy option comes with an affordable cost. |
| RAID 6 |
Its dual parity provides an improved and higher fault tolerance. Its continued operation during disk failures provides higher data availability. It also cuts down the risk of downtime in dedicated servers. |
| RAID 10 |
It provides high performance and redundancy in dedicated servers. It also can endure the failure of one disk in each mirrored pair. |
| RAID 2, 3, 4 |
These levels have very limited advantages. RAID 5 and 6 have taken the places of these levels. |
| RAID 30 |
It offers high throughput for huge sequential data transfers. It can also tolerate several disk failures in dedicated servers. |
| RAID 50, 60 | The advantages of these RAID levels are as same as RAID 30. |
Disadvantages of Raid Levels
These are the disadvantages of all the RAID levels:
| RAID Levels | Disadvantages |
| RAID 0 |
It doesn’t have any options for data redundancy in case of a single disk failure in the array. It also leads to the possibility of significant data loss in the dedicated servers. It doesn’t have any basic mechanisms for error detection or correction. |
| RAID 1 |
Mirroring in this RAID leaves only half of the storage space usable. Storage space increases hardware expenses to manage large data in dedicated servers. This also hampers data write performance compared to other types of RAID. |
| RAID 5 |
Despite good read performance, it provides a slower data write performance. If a disk fails, rebuilding the array takes much time. Also, this array has a limited fault tolerance. It leads to crucial data loss in dedicated servers if a disk fails during the rebuilding process. |
| RAID 6 |
RAID 6 needs more complex parity calculations than RAID 5 due to dual parity. It leads to a much slower write performance. It also needs more disk capacity for parity. This reduces the usable storage space in dedicated servers. |
| RAID 10 | It needs twice the number of disks for mirroring. So, it is very expensive. |
| RAID 2, 3, 4 |
These types of RAID are outdated for dedicated servers. RAID 2 is inefficient, and RAID 3 and 4 provide less flexibility. |
| RAID 30 |
The dedicated parity disks can serve as bottlenecks during write operations. This RAID array level needs a vast number of disks. That makes it very complex and expensive to use. |
| RAID 50, 60 | The disadvantages of these RAID levels are as same as RAID 30. |
Final Thoughts
RAID array levels in the data storage make your dedicated hosting better.
The best kind of RAID storage for your dedicated server choices lies in the best kind of RAID levels.
So, choosing the data storage depends on your decision only.
I hope this blog post has helped you by giving you a clear idea of the best kind of RAID hard drive.
And you get the best RAID with better dedicated hosting from Hosting Ultraso.
Our company is a well-known name in providing the best dedicated hosting. And we boast of having 119 data centers worldwide.
Get the best RAID storage with the best dedicated server provider. Make your business global.



