RAID system plays an important role in dedicated server management.
You need to host your company website on a dedicated server. They keep your resources like different multimedia files. Images and videos consist of such multimedia files. Other than that, you can also store different files like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. These important resources build your website with the help of server storage.
Data is everything on a website. It gives your website a unique identity. You can save, manage, and retrieve data through the server storage space. So, storage capacity is essential for a dedicated hosting server. It keeps your website's data, applications, and system files stored safe and secure.
So, losing your data can cost you a lot. And you don’t want that to happen to your website, do you?
RAID array is here to help you.

A software or a hardware RAID boosts the performance of your dedicated server storage.
This blog gives you a general introduction to the RAID system. Then, it’ll give you every detail on software and hardware RAID.
In the end, you’ll know more about them with a comparative analysis.
This blog will give you a clear idea of what type of RAID storage to choose. So, you will have no more confusion about it.
In this blog, you will know about:
Disadvantages of Software RAID
Disadvantages of Hardware RAID
Comparison between Software and Hardware RAID
Without further ado, let’s jump in!
A General Introduction to RAID System
Before getting into a detailed discussion, it’s important to know what a RAID system is. Or how it works, at first.
RAID means Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It is a storage technology that enhances the efficiency of storage systems.
This combines many hard drives into a single logical unit to store data. Through that function, it brings reliability to disk array systems. It makes your data storage work faster with more security. This helps improve data redundancy and increase the performance of the data storage. But these two aspects sometimes depend on the RAID level of your choice.

It serves as an important factor in data protection, too. It copies data from one hard drive to another.
But that doesn’t mean that it serves as some backup technology.
Still, it boosts the dedicated server storage with its amazing utilities and functions.
Basic Functions of RAID System
This technology works through some basic yet essential functions:
- Striping: This divides data across several disks to improve read and write speeds.
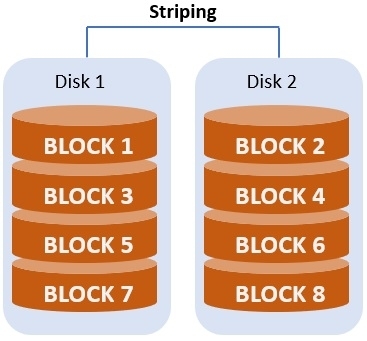
- Mirroring: It copies data across two or more disks for better data protection.
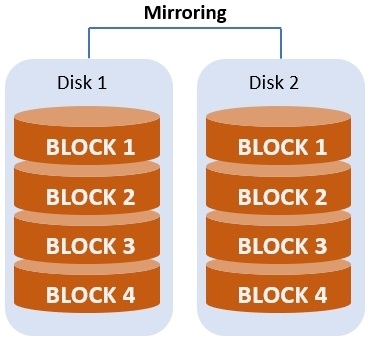
- Striping with Parity: Parity restores data in case of drive failure or loss. This function helps data and parity information stripe across three or more disks.
- Striping with Double Parity: This function is the same as striping with parity, but it takes an extra layer of parity. It provides the drive with much better protection from data loss.
- Mirroring and Striping: It mirrors the data and then stripes it on, at least, four disks. This brings redundancy and performance in the storage.
Basic RAID Levels
Basic levels of the RAID system carry out these functions. There are some common RAID levels. They are RAID 0, 1, 5, 6, and 10 (1+0).
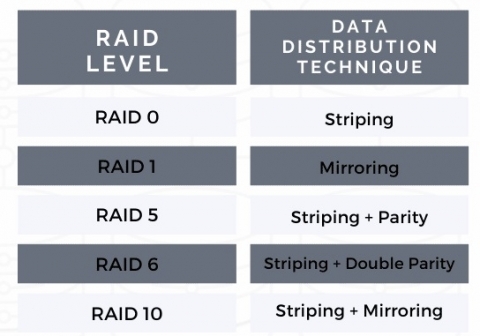
These levels provide different types of configurations in the RAID data storage. But they have a huge impact on the basic aspects of RAID.
Primary Aspects of RAID System
RAID hard drive works through some primary aspects:
- Redundancy: This feature duplicates data across several disks. This ensures data integrity in your dedicated server storage. It also makes your data available in case there is a disk failure. Mirroring or parity makes this happen.
- Performance: RAID array also distributes data across several disks. This helps improve data read or write speeds in the storage. It happens due to striping and the combined functions of mirroring and striping.
- Capacity: You also can have total storage available in the RAID system. But this depends on the RAID levels. The storage capacity varies in different levels. RAID 0 gives you the highest storage capacity. But RAID 1 provides half of the total disk.
- Fault Tolerance: This feature makes the RAID storage system continue working despite a disk failure. Different RAID levels provide various degrees of fault tolerance. Redundancy and parity operate to make it work. It becomes important for critical dedicated hosting solutions.
- Data Protection: It also protects your data from corruption or loss. It ensures that your data is safe from the terrible effects of a disk failure. Redundancy with mirroring or parity keeps your data secure.
- Hot Swapping: This replaces a failed disk in your storage without the full system shutdown. This feature is available in many RAID controllers. This is crucial to maintain uptime and data availability in dedicated servers.
- Rebuilding Process: This refers to the time of restoring the array to the state of full redundancy. This happens after a disk failure and replacement, in general. RAID levels with huge capacity take longer rebuild times. Faster rebuild times cut down the risk of data loss.
What Is Software RAID?
Software RAID means the implementation of RAID technology through software. The software runs on the host operating system (OS) of a dedicated server, in this case. It operates on the system’s CPU and memory resources. This is how it manages the system with data striping, mirroring, and parity.
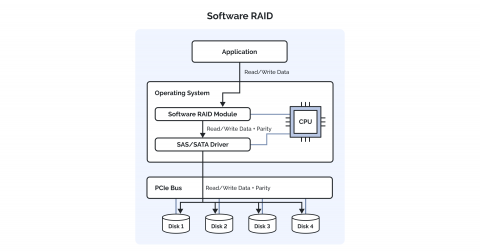
This setup combines many physical disks to make an array. It takes the help of different OS utilities or third-party software to configure. This allows creating, managing, and monitoring the RAID system. And it doesn’t take help from any specialized hardware RAID controllers.
Advantages of Software RAID
These are some of the major advantages of software RAID:
- No Hardware Dependency: A particular operating system controls running this technology. So, it doesn’t depend on any specific hardware elements. It makes moving the RAID array to another machine easier in case of server or system failure.
- OS Integration: This facility makes basic OS maintenance processes in a dedicated server more seamless. It also allows for more consistent updates, patches, and support.
- Easy Recovery: In case of system failure, you can recover data by relocating the disks to another dedicated server. This feature makes your data recovery woes vanish.
- Monitoring Tools: Many software RAID solutions offer you powerful monitoring tools. This allows you to check on the RAID status. It also makes maintenance tasks easy to handle.
Disadvantages of Software RAID
It also comes with some crucial disadvantages:
- Lack of Hardware Support: This doesn’t have the major benefits of hardware features, like battery-backed cache. That feature helps in stopping data loss during power failures in a dedicated server. This makes this RAID data storage less reliable in critical situations like this.
- Limited RAID Levels: This RAID system only supports basic RAID levels like RAID 0, 1, and 5. So, it gives you fewer advanced RAID arrays with limited efficiency.
- Limited Hot Swapping and Hot Spares: It doesn’t have a strong hot swapping feature like in hardware RAID. It is less seamless and secure which results in its lower efficiency.
What Is Hardware RAID?
Hardware RAID works through integrated RAID controllers on a dedicated server's motherboard. Those controllers manage the RAID system being independent from the host operating system. They also manage tasks like data striping, mirroring, and parity calculations.
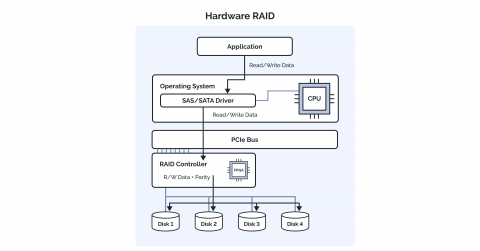
The RAID controller has its own processor, memory, and firmware. This helps offload RAID management tasks from the host system. This also provides a more structured and independent solution. And it helps manage several disk drives in a RAID setup with that solution.
Advantages of Hardware RAID
Hardware RAID gives you these advantages:
- Reliability: Some hardware RAID controllers come with a battery-backed or non-volatile cache. This prevents data loss in the cache in case of power failure. The controllers also come with advanced error detection and correction systems. This enhances data integrity and lowers the risks of data corruption.
- Hot Swapping and Hot Spares: It also supports hot swapping. This facility replaces failed drives without a full system shutdown. It also gives you the facility of hot spares. These are standby drives that take the place of a failed drive. This cuts down the downtime and improves fault tolerance.
- Advanced RAID Levels: Hardware RAID controllers give you more complex RAID levels. Those levels are RAID 6, 10, and more. This gives you more options for higher redundancy and performance in the dedicated servers.
- Improved Data Security: Some hardware RAID controllers offer you hardware-based encryption support. This gives an added layer of data security. This also doesn’t affect the performance of the system at all.
Disadvantages of Hardware RAID
It comes with some of these disadvantages:
- Potential for Single Point of Failure: The RAID controller can be the very reason for a single point of failure. The entire RAID system may be in danger if it malfunctions. It might become unavailable even if the drives are still working. Having redundant controllers can reduce the risk. But that is a complex process, and pricey to handle.
- Recovery Challenges: Data recovery in failed hardware RAID settings is more complex and expensive. The same or a compatible RAID controller can fix that. But that’s also a very high-cost affair. Complex portability options also make matters worse for data recovery in this case.
- Physical Space: It takes up more physical space within the dedicated servers. This creates problems for expanding storage capacity in a confined space.
Differences between Software and Hardware RAID
There are some major differences between these two types of RAID in dedicated servers:
| Points of Difference | Software RAID | Hardware RAID |
| Implementation | A host operating system with software resources manages this RAID. | A dedicated RAID controller card on the motherboard manages this RAID. |
| Performance | It uses the host system’s CPU and memory for its operations. | It uses an integrated processor and memory on the RAID controller. |
| Cost | It’s more cost-effective. | It’s very expensive. |
| Ease of Setup and Management | It’s easy to set up. | It has a very complex setup. |
| Scalability and Flexibility | It’s easier to adjust and expand. | It has limited flexibility due to the need for specific RAID controllers. |
| Performance Impact at the Time of Rebuilds | Rebuild operations have a significant impact on system performance. | Rebuild operations have the lowest impact on system performance. |
| Fault Tolerance and Recovery | These depend on the capability of the OS. | It offers a stronger fault tolerance and faster recovery. |
| Compatibility | It’s more compatible with different systems and platforms. | It deals with significant compatibility issues with different systems and platforms. |
| Bootability | It doesn’t have booting support in the RAID array. | It has bootable RAID arrays. |
Final Thoughts
There are pros and cons in both software and hardware RAID. But both of them perform the essential functions of RAID in their own way.
So, to choose between one of them is really up to you.
RAID boosts your businesses of any shapes and sizes. It strengthens dedicated server performance in a significant manner.
I hope this blog has helped you to make a steady decision from your side.
Also, worth noting…
We, at Hosting Ultraso, provide dedicated hosting all around the world.
You get the best facilities of 119 data centers worldwide.
And dedicated hosting gets better with RAID storage.
Get the server solution from us with the best RAID system. Choose us as the best dedicated server provider. Broaden your business around the world.



